Pre-processing Point Clouds
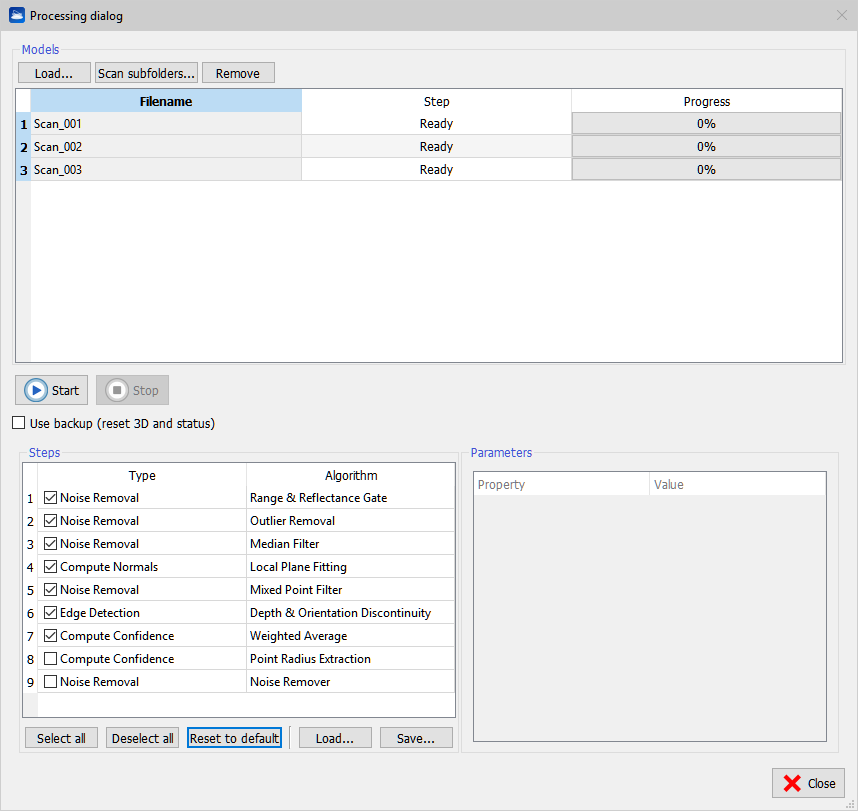
During preprocessing Reconstructor® applies a set of algorithms to the range scans, which extract information that is needed during further processing of the data. Press Load to add an external grid point cloud or Scan subfolders to find automatically all grids in a folder and its subfolders.
Press Remove to remove undesired grids. It is possible to process grids present in the current project by selecting Pre-process from the contextual menu of the grid item in the Project Window. In this case, when the processing is finished, the grid in unloaded from the project to free memory. Please force the reloading to refresh the rendering. Press Start to run the processing. This plug-in creates a separate thread for each grid so if multiple CPUs are available the processing is sped up proportionally.
All steps are applied consecutively to the selected grid by pressing the Select All button.
Reconstructor® never overwrites the original data. The first time the pre-processing begins, a backup of the data is created. By default the pre-processing pipeline starts from the data in its current state. If Use backup is checked, the pre-processing reads the backup data.
To modify the pre-processing parameters press Advanced, then select one or more rows in the list of models with [Ctrl] or [Shift] keys, then select a step of processing. The parameters are updated for all the selected models. A step algorithm can be changed by clicking the algorithm name, a combo box of available algorithm is shown. A step can be skipped by unchecking it.
Noise Removal
Range & Reflectance Gate
Min/Max range [m]: lower/upper threshold of the range. All pixels outside this range will be filtered.
Min/Max reflectance [0÷1]: all measurements that have an intensity value outside the given interval will be filtered.
Outlier Removal
Outlier removal is a Noise Removal filter that permits to delete the lonely points outside a detected surface, following this concept:
every point is investigated, and the N. points (i.e. Neighbourhood Size 24 ) closer to it in the 3D space are detected. Also these points have N. points closer to them. If some point has neighbors, but these neighbors haven't it as a neighbor (so there aren't Incoming Edges), it means that this is an outlier.
The min. outlier likelihood is the probability that a point is an outlier: [1- (N. of Incoming Edges)/(Neighbourhood Size)]
Lower is this value higher the number of outlier points, starting from isolated points, until groups and edge points.
Neighbourhood size [pix]: pixels frame close to the current pixel.
Min. outlier likelihood [0÷1]: probability that a point is an outlier = [1- (N. of Incoming Edges)/(Neighborhood size)]
Noise Remover
The noise remover filter removes points that don't match the local geometrical behavior of the point cloud.
For each point, it analyzes the surrounding space looking for planar and linear features at different scales because, as an example, a point near an edge will looks like lying on a plane if the surrounding space in close proximity is considered, while it looks like lying on a more complex geometrical structure (e.g intersecting walls) if a wider portion of space is considered.
The Minimum search radius and Maximum search radius parameters control this analysis providing the boundaries within which the algorithm varies the scale. The algorithm will try to estimate a local surface and if it is not able to do so, it will leave the point untouched to avoid removing sharp features like wall edges. Even if the quality of the denoising improves with a wide search radius, increasing its value, though, has an high computational cost dependent on the point cloud density and ranges wider than the actual geometrical features provide very little to no improvements. The algorithm removes the analyzed point if its distance from the estimated surface is above the Threshold parameter [m]. It is possible to control the aggressiveness of the filter through this parameter. For points in isolated regions of space it doesn't make sense to look for geometrical features but it may be necessary to remove them. If a point has less than an Isolated Threshold number of neighbors within the Maximum search radius, it gets classified as an isolated point and removed if the check box Remove isolated points is set.
![]() This filter thins noisy point clouds. It is very useful for indoor or outdoor mobile mapping surveys.
This filter thins noisy point clouds. It is very useful for indoor or outdoor mobile mapping surveys.
Median Filter
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Mixed Point Filter
Useful as a relative depth discontinuity filter.
Min incident angle [deg]: if the line of sight from the origin of the grid to the point has incident angle to the local surface less than this value, the point is filtered.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Compute Normals
Local Plane Fitting
Computes the local surface tangent plane for each point, based on the neighborhood of the pixel.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Neighborhood size [pix]: pixels frame close to the current pixel.
Compute also curvature: set TRUE to compute it.
Adjust normals' verse in handheld scans: set TRUE if processing handheld scans.
Edge Detection
Depth & Orientation Discontinuity
Computes geometrically significant line features from the point cloud data. Two types of edges are extracted:
- Depth discontinuities (or jump edges) that occur where the scanner hits an occlusion and therefore the measured range jumps from a foreground to a background value.
- Orientation discontinuities (or crease edges) that occur where the object has a sudden change of its surface orientation.
The extracted edges are stored as a bit flag for each point.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Min depth discontinuity to flag [m]: absolute depth discontinuity to filter.
Min orientation discontinuity to flag [deg]: the current point is marked if its normal differs from the adjacent ones of at least this angle.
Compute Confidence
Weighted Average
Computes a confidence value for each measurement, which is a measure for the reliability of the given range measurement. The accuracy does not only depend on the type of scanner used, but amongst others also on the following factors:
- The incident angle between the laser beam and the tangent plane of the target
- The distance to the target
- The material of the object and therefore the intensity of the reflected signal
The confidence value is computed as a weighted sum of the surface normal, the range value and the reflectance value.
Min/Max range [m]: the range is weighted by normalizing it within this interval.
Scale factor: the confidence value calculated for each pixel is multiplied with this scale. Thus the user has the possibility to decrease or increase the weight for a given scan manually, for example because a scanner with higher accuracy has been used during acquisition.
Weight of range/reflectance/inclination: modify the weight as desired.

Save and load your custom settings for specific type of survey and elaboration.
Point Radius Extraction
The Point Radius Extraction define the amount of surface that every point can represent. The Max. Radius is the maximum radius of the aforementioned area (it's suggested to not change this value).
The result of this value is not directly understandable but it'll be useful to future operations.
