Mesh Editor

This dialog is an environment designed for advanced mesh editing operations. It works on one mesh at a time. It is accessible from Data management→Meshing→Mesh editor, from the corresponding button in the top toolbar, or from the context menu of any mesh in the project window.
From top to bottom, the dialog displays the mesh's full path, then a toolbar with groups of buttons, then a navigable 3D view to show the mesh, and lastly information on triangles and vertices count.
File
|
|
This button group provides the Save and Save as options. These are needed because the edits performed in this dialog are not automatically transferred to the mesh in Reconstructor®'s project. In fact, if you close the dialog you are asked if you want to save or discard the changes. |
Geometry
This button group allows you to switch between the three visualization possibilities of a mesh:
|
|
only vertices, |
|
|
only triangle edges (wireframe), |
|
|
or the triangle's faces (flat). |
|
|
The button backface allows you to show or hide the triangles' backface. |
Coloring
|
|
The first two buttons allow you to change how to color the mesh: using the colors associated to the vertices, or using a gray color that changes only according to the triangles' inclination with respect to the light source. |
|
|
The button boundaries highlights in bright red all the boundary edges of the mesh, and it is particularly useful to quickly spot where the mesh has holes to fill or imperfect boundaries that should be corrected. |
Selection
Here you can use several selection modes.
|
|
When the button None is checked, you can navigate the mesh. |
|
|
By clicking Triangles, you start selecting the mesh triangles by drawing a rectangle on the viewport. Selected triangles are highlighted in yellow. |
|
|
The button Invert enables you to invert the current triangles selection. |
|
|
The button Boundary turns on another selection mode. In this mode you can select one of the circular boundaries that the mesh has. Boundaries are polygons formed by those mesh edges who belong to one and only one triangle. A closed mesh has no boundaries. Boundaries selected in this mode may delimit a hole that you want to close. After selecting the hole's boundaries, you can click on Close boundaries in the Editing button group. |
|
|
By pressing the button Close all the triangles will be deselected. |
![]() When selecting and managing triangles the Flat geometry must be selected in order to visualize the triangles' surfaces colored in yellow after the selection process.
When selecting and managing triangles the Flat geometry must be selected in order to visualize the triangles' surfaces colored in yellow after the selection process.
Editing
|
|
Once you have selected some triangles with the command Triangles, you can delete the selected triangles with Delete triangles. |
|
|
By using the Close boundaries button you can close a mesh hole whose boundaries have been selected with Boundary command.
|
Filter
This button group contains four functions:
|
|
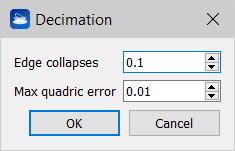
The Decimation tool allows you to simplify your mesh substituting small triangles with bigger ones if the mean-square error introduced in this way is smaller than a user-customizable threshold.. Simplification is based on conveniently collapsing edges among triangles. For each edge shared by two triangles, Reconstructor® assesses whether collapsing it or not. Collapsing an edge means assigning the edge's two vertices to coincide in the edge's middle point, and adjusting all neighboring triangles consequently. If the quadratic error between the surface before and the surface after the collapsing is below the parameter Max quadric error of the dialog, then the edge is collapsed. The algorithm tries to collapse a percentage of edges as specified by the parameter Edge collapses, where 0.1 stands for 10%. |
|
|
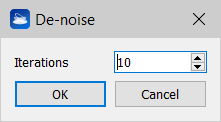
This De-noise algorithm allows you to de-noise your mesh, meaning to iteratively eliminate spikes from your mesh, without changing the surface's volume. A smoothing filter is run on the mesh for as many times as the parameter Iterations says. This filter has anisotropic properties: it eliminates the spikes without changing the surface's volume. Along the iterations, it distributes the volume from the spike to the neighboring triangles. |
|
|
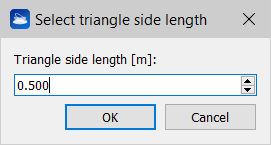
The Triangles remover tool select the triangles that have at least one side greater than the entered threshold value Triangle side length in meters.
|
|
|
The Trim mesh tool select the triangles along the boundaries of the mesh. These triangle have at least one side not connected with another triangle.
|
If the MINING add-on is activated, also the Crest and toe command will be included in this section. You can access it through the dedicated command in the MINING toolbox bar.
|
|
Crest and toe is a semi-automatic technique to detect crests (prominent mesh edges) and toes (reentrant mesh edges). When you open this dialog, the crests and toes are calculated and drawn in the mesh editor. Crests are drawn as blue polylines, Toes are in red. Crests and toes can be then saved as polylines. The idea is that tool shows you an initial extraction of crests and toes, successively you refine the parameters of extraction and see the effects of your changes in real time. You can refine the parameters until you are not satisfied, and then save the crests and toes as polylines in the project. The parameters of crests&toes extraction you can modify regard the curvature, the horizontality, the length of the edges and the gaps between them. While you modify the parameters and recompute the crests&toes, you can choose to turn on or off the visualization of the crests, the toes and the mesh, via the three check-boxes in the Draw groupbox at the bottom of the dialog. Curvature filter The topmost slider of the dialog allows you to modify a threshold on the curvature of the crests and toes. Crests and toes are edges shared by your mesh's triangles. Each edge has a curvature associated, depending on the angle between the two associated triangles. A threshold on the curvature filters out the smoother edges and leaves only the steeper ones, which normally are the most important. Scroll the slider to see the effect of the threshold in real time. Orientation filter Below the curvature filter, you can also activate a orientation filter. This filter keeps only the edges whose angle with respect to the horizontal plane is close to the angle you indicate with the slider. In this way, you can choose to keep only the horizontal edges, or the vertical ones, or the ones with a given inclination. Close gaps in edges Sometimes crests and toes come in many segments with small gaps among them. In the groupbox Close gaps in edges you find a tool to close those gaps and get the crests and toes as continuous polylines. You can set the maximum gap distance to close, and press Apply. Reconstructor will start closing the gaps from the smallest to the biggest, without creating loops or bifurcations. Delete short edges In the Delete short edges a tool comes to filter out polylines whose total length is less that the specified parameter. Normally you want to discard short edges because they are not the main ones. The main ones should instead be found by closing the gaps among them. General procedure As general procedure, we advice to use the described filters in the order given above, and to close and open the dialog if the result is not satisfactory. Once the extracted crests and toes are good enough to describe the important edges of your model, press Save as polylines at the bottom of the dialog. New polylines with the crests and toes will be added to your project. |