Pre-processing Point Clouds
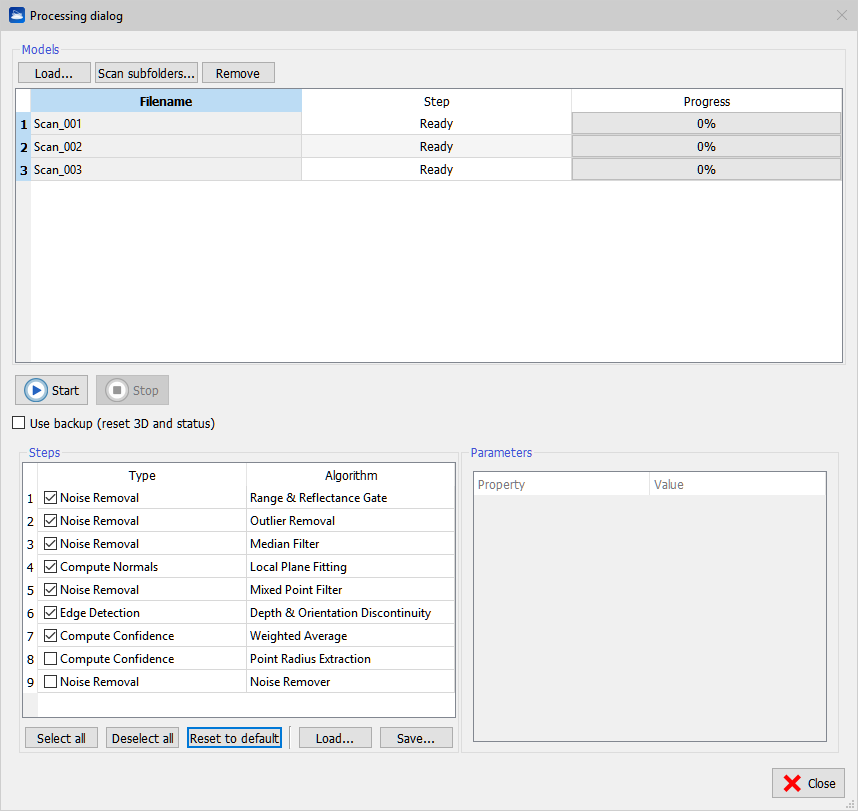
During preprocessing Reconstructor® applies a set of algorithms to the range scans, which extract information that is needed during further processing of the data. Press Load to add an external grid point cloud or Scan subfolders to find automatically all grids in a folder and its subfolders.
Press Remove to remove undesired grids. It is possible to process grids present in the current project by selecting Pre-process from the context menu of the grid item in the Project Window. In this case, when the processing is finished, the grid in unloaded from the project to free memory. Please force the reloading to refresh the rendering. Press Start to run the processing. This plug-in creates a separate thread for each grid so if multiple CPUs are available the processing is sped up proportionally.
All steps are applied consecutively to the selected grid by pressing the Select All button.
Reconstructor® never overwrites the original data. The first time the pre-processing begins, a backup of the data is created. By default the pre-processing pipeline starts from the data in its current state. If Use backup is checked, the pre-processing reads the backup data.
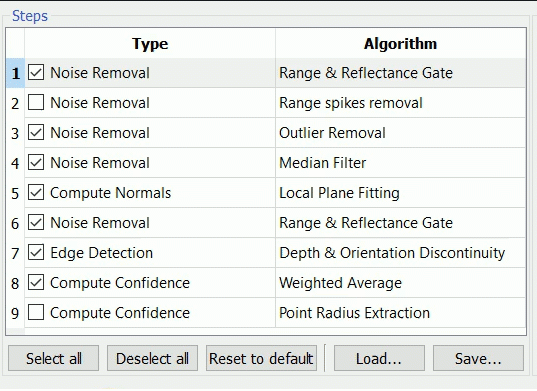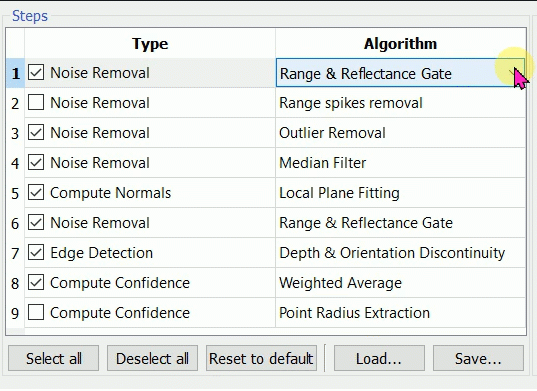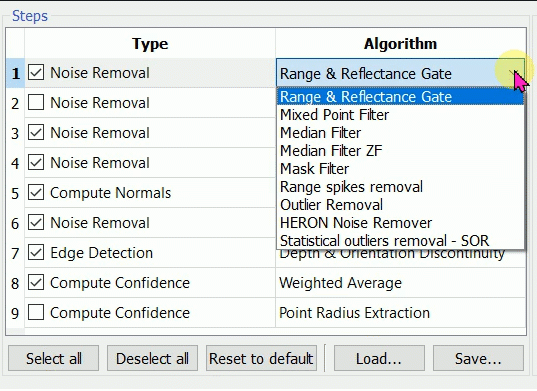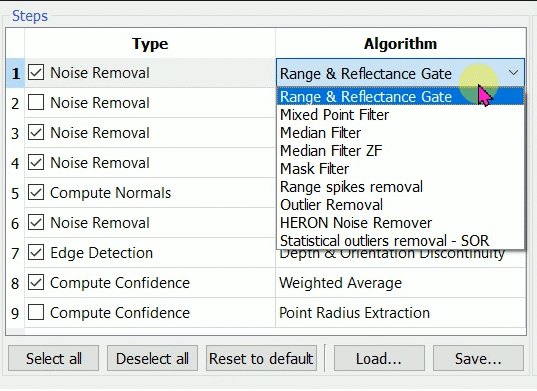
![]() A step algorithm can be changed by clicking the algorithm name, a combo box of available algorithm is shown. A step can be skipped by unchecking it.
A step algorithm can be changed by clicking the algorithm name, a combo box of available algorithm is shown. A step can be skipped by unchecking it.
The drop-down menu appears if clicking the Type item and the arrow on the right:
Noise Removal
Range & Reflectance Gate
Min/Max range [m]: lower/upper threshold of the range. All pixels outside this range will be filtered.
Min/Max reflectance [0÷1]: all measurements that have an intensity value outside the given interval will be filtered.
Outlier Removal
Outlier removal is a Noise Removal filter that permits to delete the lonely points outside a detected surface, following this concept: every point is investigated, and the N. points (i.e. Neighborhood Size 24 ) closer to it in the 3D space are detected. Also these points have N. points closer to them. If some point has neighbors, but these neighbors haven't it as a neighbor (so there aren't Incoming Edges), it means that this is an outlier.
The min. outlier likelihood is the probability that a point is an outlier: [1- (N. of Incoming Edges)/(Neighborhood Size)]
Lower is this value higher the number of outlier points, starting from isolated points, until groups and edge points.
Neighborhood size: number of points closest to the current point. The minimum settable value is 11, while the maximum value is 99.
Min. outlier likelihood [0÷1]: probability that a point is an outlier = [1- (N. of Incoming Edges)/(Neighborhood size)]
Mixed Point Filter
Useful as a relative depth discontinuity filter.
Min incident angle [deg]: if the line of sight from the origin of the grid to the point has incident angle to the local surface less than this value, the point is filtered.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Please note that this filter works only on grid point clouds.
Median Filter
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Please note that this filter works only on grid point clouds.
Mask Filter
Loading a 2D image file (Mask file) in which some points are colored in black (RGB = 0,0,0), the corresponding points in the 3D point cloud will be deleted.
![]() The 2D image must derive from the 2D grid (look at Save Image in Edit 2D), then processed in a photo editing software.
The 2D image must derive from the 2D grid (look at Save Image in Edit 2D), then processed in a photo editing software.
Range Spikes Removal
This filter attempts to remove range discontinuities by looking at the average range of a neighborhood of each point. Range discontinuity threshold is set to 200m and can be changed. Neighborhood size is set to a 10 x 10 square around any given point and can be changed by editing the "mask size parameter". Please note that this filter works only on grid point clouds.
HERON clean geometry
This filter is specifically designed for HERON Data and it is automatically embedded in HERON data import workflow.
The Heron clean geometry tool improves the underlying geometry when clearly characterized but does not reduce point density. If the points cannot define a clear local geometry, the filter leaves the local data untouched.
The filter performs best on planar or smooth varying surfaces like, for example, walls, stairs, furniture and pipes.
By flagging (True) Use normals the filter will use normals to select the best set of points from which derive the local geometric behavior. It may help to better preserve certain features like two sides of the same wall. It should be always used unless the normal layer of the dataset is particularly unreliable.
By flagging (True) Out of core the filter will keep all the data in the main memory in order to achieve better performance. Out of core computation allows the filter to keep only the necessary data in memory when the dataset is too large for the main memory. It is, in general, slower than the non out of core version, therefore not enabled by default.
The Search radius [m] value controls the size of the neighborhood around each point. It should match with the scale and point density of the dataset. The default value of 5 cm is optimal for a Heron's acquisition of a building. A lower value should be used if the dataset represents smaller object with higher point density.
The Noise standard deviation [m] value represents the expected sensor noise level. When the dataset represents real world complex geometries it is difficult to identify what is noise and what are real data. This option provides a hint to the filter to differentiate the two. By default a standard value is suggested, but it can be changed according to the sensors.
Statistical outliers remover - SOR
This filter firstly computes the average distance of each point to its neighbors (where the number of nearest neighbors is defined by the Neighborhood size). After that it rejects the points that are farther than the average distance plus a number of times (Standard deviation threshold) the standard deviation.
![]() The default Neighborhood size is an optimal value, especially for HERON Data. Increasing it, the computation time will increase and a much better result is not guaranteed in some cases. Decreasing it a worst result is possible.
The default Neighborhood size is an optimal value, especially for HERON Data. Increasing it, the computation time will increase and a much better result is not guaranteed in some cases. Decreasing it a worst result is possible.
Compute Normals
Local Plane Fitting
Computes the local surface tangent plane for each point, based on the neighborhood of the pixel.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Neighborhood size [pix]: pixels frame close to the current pixel.
Compute also curvature: set TRUE to compute it.
Adjust normals' verse in handheld scans: set TRUE if processing handheld scans.
Edge Detection
Depth & Orientation Discontinuity
Computes geometrically significant line features from the point cloud data. Two types of edges are extracted:
- Depth discontinuities (or jump edges) that occur where the scanner hits an occlusion and therefore the measured range jumps from a foreground to a background value.
- Orientation discontinuities (or crease edges) that occur where the object has a sudden change of its surface orientation.
The extracted edges are stored as a bit flag for each point.
Mask border [pix]: the kernel of the filter is a square mask (of side 2∙border+1) centered at the current pixel.
Min depth discontinuity to flag [m]: absolute depth discontinuity to filter.
Min orientation discontinuity to flag [deg]: the current point is marked if its normal differs from the adjacent ones of at least this angle.
Compute Confidence
Weighted Average
Computes a confidence value for each measurement, which is a measure for the reliability of the given range measurement. The accuracy does not only depend on the type of scanner used, but among others also on the following factors:
- The incident angle between the laser beam and the tangent plane of the target
- The distance to the target
- The material of the object and therefore the intensity of the reflected signal
The confidence value is computed as a weighted sum of the surface normal, the range value and the reflectance value.
Min/Max range [m]: the range is weighted by normalizing it within this interval.
Scale factor: the confidence value calculated for each pixel is multiplied with this scale. Thus the user has the possibility to decrease or increase the weight for a given scan manually, for example because a scanner with higher accuracy has been used during acquisition.
Weight of range/reflectance/inclination: modify the weight as desired.

Save and Load your custom settings for specific surveys and elaborations.
Point Radius Extraction
The Point Radius Extraction define the amount of surface that every point can represent. The Max. Radius is the maximum radius of the aforementioned area (it's suggested to not change this value).
The result we'll be useful to splat rendering.
